11 Lean Proteins You’ll Want to Add to Your Diet

Whether you want to maintain your weight, lose a few pounds, increase your energy level or build muscle, you’ll want to make room on your plate for whole food sources of protein.
But like most things, not all proteins are created equal.
Lean proteins are your best bet, and we’ll break down everything you need to know about this superior protein choice and why you should increase your protein intake.
What Is a Lean Protein?
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) definition of a lean meat protein is one that contains less than 10 grams of total fat and fewer than 4.5 grams or less of saturated fat per portion [100 grams], says Diana Gariglio-Clelland, R.D., a registered dietitian in Washington.
11 Lean Protein Foods
Plants are naturally low in fat, so we’ve spotlighted some grains and legumes that are particularly high in protein.
Below you’ll find the best sources of protein and what kind of nutrients they contain.
1. Boneless Skinless Chicken Breast

Per 3.5-ounces, cooked: 30g protein
The boneless skinless chicken breast is a staple of fitness-friendly and weight-loss eating plans for a reason: It’s sky-high in protein and low in calories. Plus, like all meats, it’s a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids.
“Poultry provides vitamin B3 and B6, which helps with carbohydrate metabolism,” says Anis Rehman, M.D. “It also provides selenium, which is an excellent antioxidant.”
Grill, roast, bake, or steam it — just make sure to remove the skin first.
2. White Fish
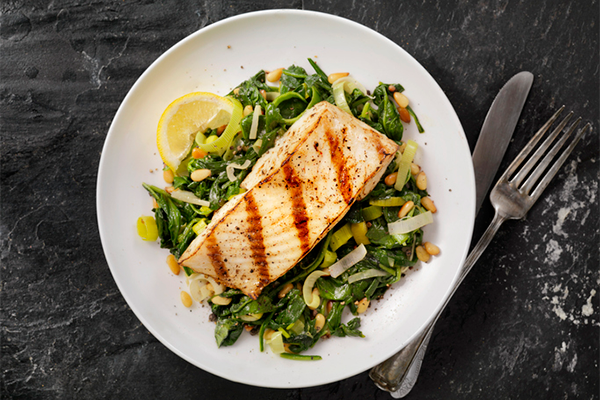

Per 3.5 ounces, cooked: 19g protein
White-flesh fish — e.g. tilapia, cod, flounder, and pollock — is protein rich and very lean, with only about 100 calories per 3.5-ounce serving.
Salmon isn’t technically a lean protein, because a 100-gram serving contains about eight grams of fat.
However, that’s heart-healthy fat, and salmon contains more omega-3 fatty acids than white fish, so it’s still an excellent option for your diet.
3. Pork Loin
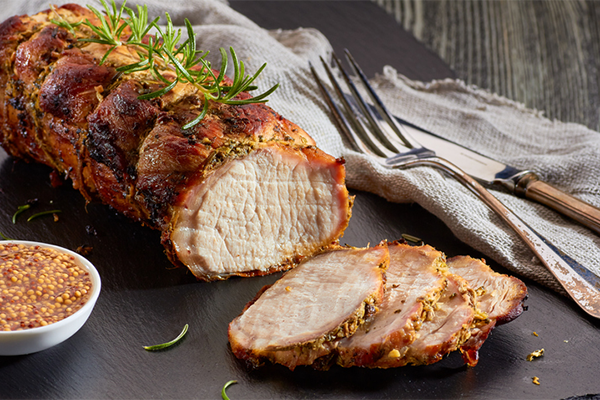

Per 3.5 ounces, cooked: 28g protein
The old ad campaign that dubbed pork “the other white meat” was on to something.
Lean cuts of pork loin have almost as much protein as chicken, are an excellent source of vitamin B6, and are a good source of potassium and zinc.
To ensure you’re buying lean pork, look for the words “loin” or “round” on the label.
4. Lean Beef
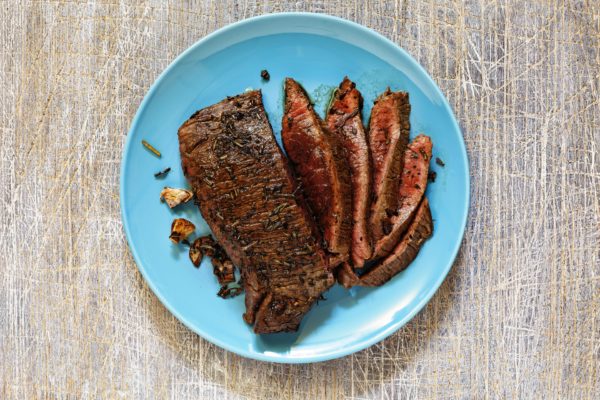

Per 3.5 ounces, cooked: 23g protein
“Lean meat provides an excellent source of protein and iron with fewer calories and less fat than non-lean meat sources,” says Rehman, and this extends to red meat like beef.
When buying ground beef, 95% lean or more counts as “lean protein;” opt for grass-fed beef to get the most heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
5. Tuna
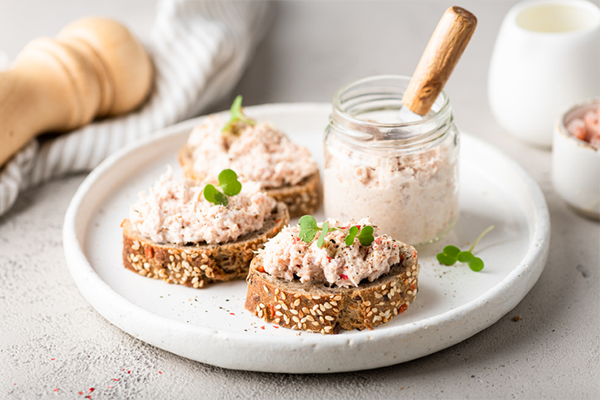

Per 3.5 ounces, cooked: 19g protein
Canned tuna is an extremely convenient source of lean protein, for lunches or a post-workout snack, with less than two grams of fat per serving.
It’s also a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and selenium. Concerned about mercury content?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says canned light tuna is low in mercury, and it’s safe to eat two to three servings per week.
This is not the same for albacore/white tuna, which is higher in mercury — it’s recommended you limit to one serving per week.
6. Shrimp
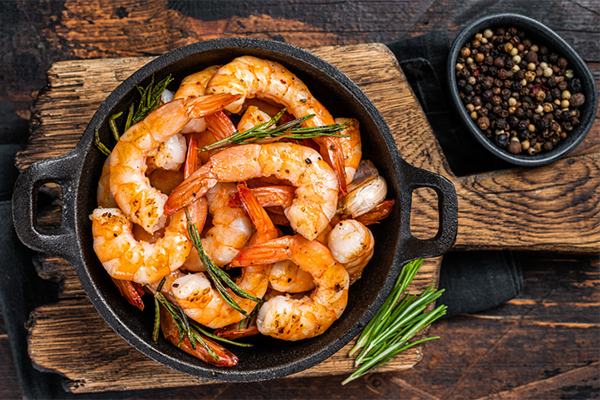

Per 3.5 ounces, cooked: 16g protein
Shellfish, including shrimp, is a highly nutritious source of protein.
Just one serving of shrimp provides more than half your daily recommended allowance of selenium and vitamin B12.
7. Plain Greek Yogurt
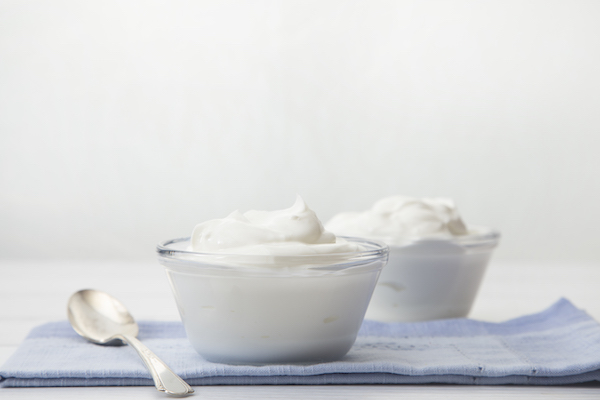

Per 6-ounce container: 17g protein
A serving of plain Greek yogurt packs 17 grams of protein, compared to nine in regular yogurt. It’s because Greek yogurt is strained, and therefore thicker and more concentrated.
Avoid flavored yogurts (extra added sugar), but feel free to add fresh fruit, cinnamon, or slivered almonds.
8. Beans
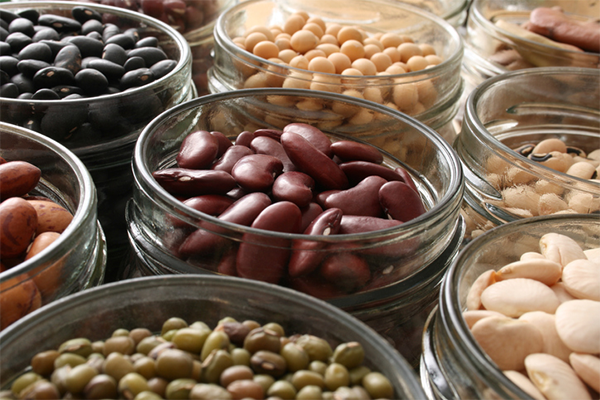

Per 1/2 cup, cooked: 6g protein
An excellent lean-protein base for soups, stews, or chili (or a topper for salads), beans have five grams of protein in each half-cup.
And unlike most other lean proteins, they’re also a source of fiber providing six grams per serving.
9. Tofu
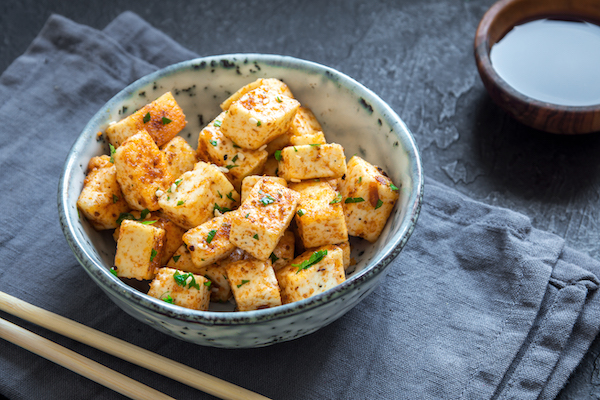

Per 1/2 cup: 10g protein
There’s a reason why tofu is a vegetarian’s go-to meat substitute — its high protein content.
A half-cup serving has nine grams, along with 4.5 grams of fat and only 75 calories.
10. Farro
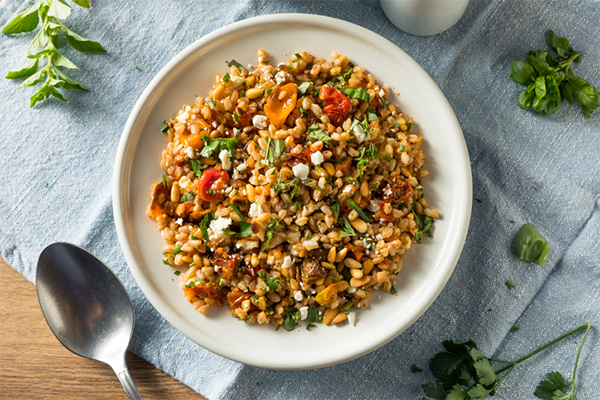

Per 1/2 cup, cooked: 10g protein
If “super grains” existed, farro would likely fall in that bucket. This ancient grain has twice the protein found in quinoa.
Like most other whole grains, farro also provides fiber — five grams per half cup.
11. Cottage Cheese
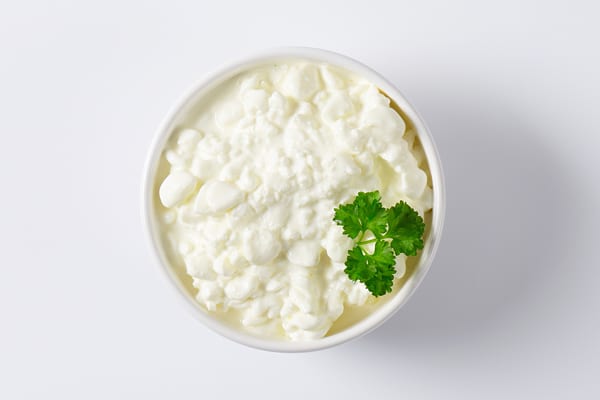

Per 1/2 cup: 11g protein
The favorite of 1970s dieters deserves to be pulled out of the archives and back into your refrigerator. For a dairy product, cottage cheese is exceptionally lean — less than five grams of fat, and about 90 calories per cup serving.
What Are the Benefits of Lean Protein?
Here are some reasons why you don’t want to skimp out on lean proteins in your meals.
1. It may increase satiety
As an essential macronutrient, protein helps fill you up, and lean versions do this with less fat and fewer calories.
2. It may be beneficial to maintain and build muscle
“Protein is an essential building block for muscles,” says Samantha Presicci, M.C.N., R.D., L.D., C.P.T., lead registered dietitian with Snap Kitchen in Austin, Texas.
3. It is believed to be linked to weight loss
Because it keeps you feeling full and can help build muscle, lean protein can be a tool to help you lose weight.
4. It can help to keep the body running efficiently
“Some proteins act as enzymes, which help with thousands of biochemical reactions in the body,” says Presicci. “They’re essential for things like digestion, energy production, blood clotting and muscle contraction. Some proteins also act as hormones, helping communication between cells, tissues and organs.”